If you’re wondering how to wire a rotary phase converter, don’t worry – This blog post will show you exactly how to wire a rotary phase converter using easy-to-follow instructions.
We will also provide a breakdown of the different parts of a rotary phase converter so that you are fully aware of what is happening inside the device. Finally, we will provide some tips on troubleshooting any issues you might encounter. So if you’re looking to wire a rotary phase converter correctly, look no further.
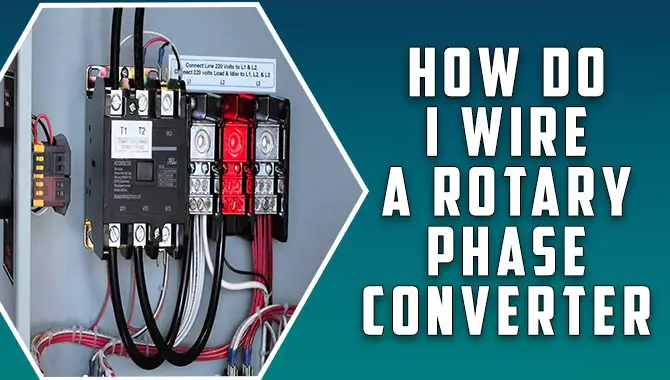
What Is A Rotary Phase Converter?

If you’ve ever been curious about how a rotary phase converter works, this blog is for you! This component is used in electric motors and other devices to create direct currents (DC). When connecting two coils in series, the rotating field created by the commutator will cause one coil to rotate faster than the other.
This difference in speed between the two coils causes the output voltage to be constant, but the polarity will change with each cycle due to this difference in speed between the two coils. So, if you want to learn more about how rotary phase converters work, read on.
What Purpose Does A Rotary Phase Converter Serve?

A rotary phase converter is a device that can use to convert single-phase AC into three-phase AC or vice versa. It can also use to change the frequency of an electric current. This makes it useful in industrial applications requiring high power and precision.
Besides being used for controlling motors, lighting, and other electrical equipment, a rotary phase converter is also commonly found in medical equipment such as pacemakers and defibrillators.
Things To Keep In Mind While Wiring A Rotary Phase Converter

When wiring a rotary phase converter, it is essential to take note of the following points:
- Make sure to prevent any damage to wiring correctly.
- The converter needs lots of power, so ensure the wiring is strong enough.
- Terminals and wires must be insulated well against heat, cold, and sparks.
- Wiring must be kept neat – no unneeded clutter!
How Does A Rotary Phase Converter Work?

If you’re working with an AC signal, you need a rotary phase converter. This device is a simple yet powerful tool that splits the AC signal into two parts. The devices consume the first part that needs an AC signal in the voltage range of voltage-controlled AC (VAC) systems, such as power tools.
The devices consume the second part requiring an AC signal in the frequency range of low-voltage AC (LVA) systems, such as refrigerators and air-conditioners. Why use a rotary phase converter? Well, it does a great job of converting an AC signal into two separate DC signals that can be sent to different devices.
This is important because it allows you to use other AC systems with the appropriate devices. Additionally, the rotary phase converter is a simple device that can install quickly, making it ideal for residential and small- to medium-sized businesses.
How Does It Work?
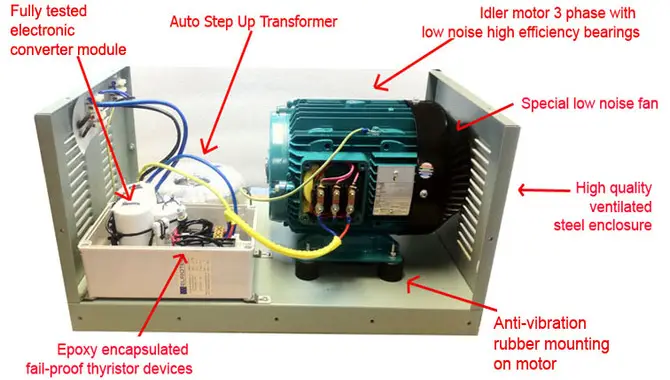
One of the most common uses of a phase converter is to change AC into DC. This happens by using a coil of wire that creates an electrical current in response to the rotating magnetic field. The motor inside the phase converter helps turn this current into a direct current, which can use for various purposes.
Types Of Rotary Phase Converters
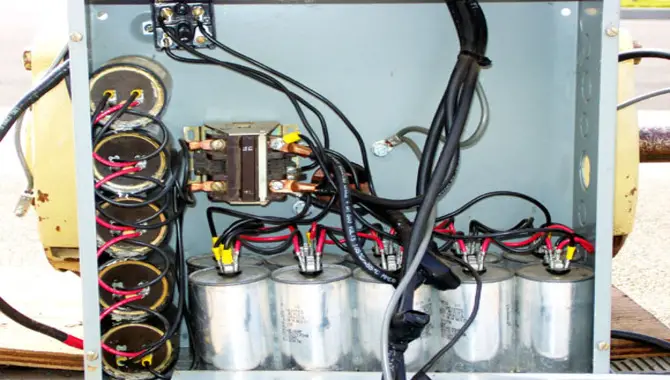
Rotary phase converters are devices that change the frequency of an electric signal. They come in two types – ferroelectric and piezoelectric. Ferroelectric rotary phase converters work more accurately but are less stable than piezoelectric ones.
Piezoelectric rotary phase converters use a set of rotating discs to change the direction of the electric current, which powers electronic equipment or motors.
What Are The Parts Of A Rotary Phase Converter?
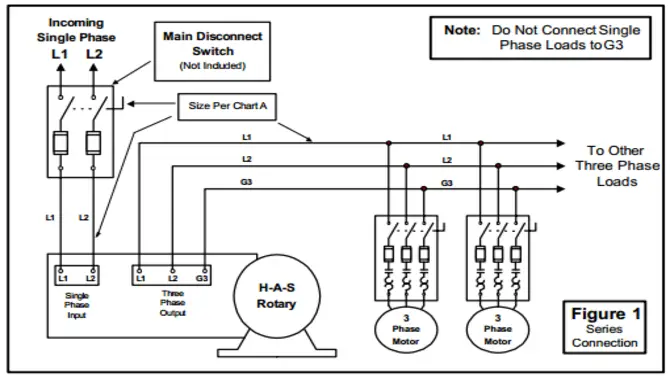
Wiring a rotary phase converter can be tricky, so it’s essential to know the parts. The contacts are what send current through your wiring to create power. The stator creates the rotating magnetic field while the rotor transfers this field to the commutator, where it’s transformed into DC electricity.
A rotary phase converter is an electrical device that changes the format of an AC signal to DC. It has four main parts: the stator, rotor, commutator, and contacts. If you’re unsure how to wire a rotary phase converter, don’t worry – our blog will guide you through the process step-by-step. So, don’t wait any longer and start wiring your rotary phase converter today!
a) The Rotor

The rotor is a device that helps to convert electric power into mechanical power. The disks rotate at high speeds to create the above statement and produce electrical energy. This electrical energy can then use to turn physical objects or machines.
b) The Windings
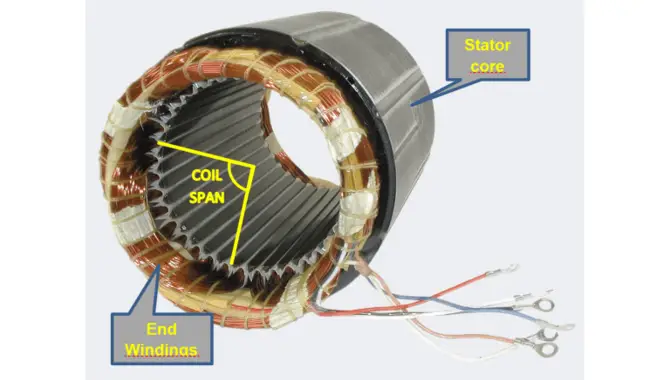
A rotary phase converter is a transformer that changes the frequency of an alternating current (AC) signal. This type of transformer has two coils – one on top of the other with different winding arrangements.
The critical difference between these coils is that the lower coil turns by a rotating magnetic field while the upper coil turns by an electric current. Depending on your specific needs and requirements, there are various ways to wire this type of transformer:
taps, lugs, or through-holes. It consists of two rotating coils, one on top of the other, which, when connected, create a resonant frequency capable of being converted to DC voltage.
c) The Stator

The stator is the main component of a rotary phase converter and converts electrical power to rotational motion. This helpful energy uses to turn the rotor, then produce valuable electricity. The stator can make from many different materials, but steel is most common due to its high durability and reliability.
d) The Pole Pieces

A rotary phase converter comprises two main components- the pole pieces and the transformer. The converter can cause instability and failure when these do not correctly align. The pole pieces need to position to make contact with each other for the transformer to work correctly, known as the resonant frequency.
If this happens incorrectly, the voltage will become excessive, and damage may occur. Additionally, keeping a regular check on alignment is essential as changes over time could also lead to issues down the line.
How To Wire A Rotary Phase Converter
Wiring a rotary phase converter can be a bit of a challenge, but that’s why we’re here to help! This article will teach you how to wire a rotary phase converter, starting with the basics. Remember to use heat-shrink tubing when connecting wires to the components of the rotary phase converter, and have fun!
Once you understand the wiring process, follow the instructions that correspond to the type of wiring you need. Have fun, and thank us later – we did help make wiring a rotary phase converter much less stressful!
Components Of A Rotary Phase Converter

To wire a rotary phase converter, you first need to identify the required voltages (AC and DC) and then find the correct wires to connect them. The three main components of a rotary phase converter are the stator, rotor, and magnet. The stator is responsible for generating the AC voltage and converting it into DC.
The rotor is responsible for translating that voltage into rotating energy which an electronic device or generator can use. Finally, the magnet helps in connecting these three parts so that they can generate electricity.
Steps To Wire A Rotary Phase Converter
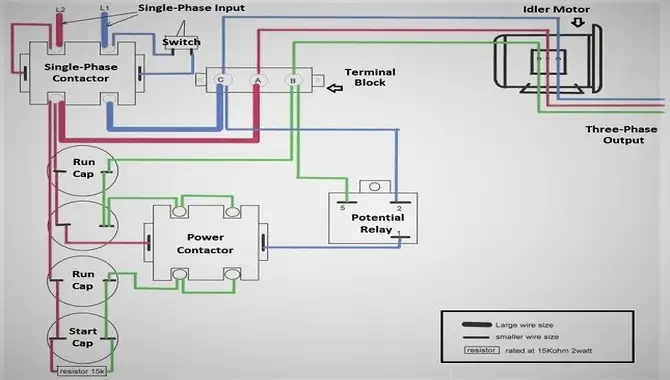
Wiring a rotary phase converter is not easy, so taking the necessary steps before starting is essential. Here are some tips that will help you along the way:
- First, you will need to draw a circuit diagram of your rotary phase converter and identify all the components involved.
- Once you clearly understand the circuit, it’s time to connect all the wires and test your installation for any errors or malfunctions.
- Next, find your device’s correct wires and connectors – sometimes, this requires detective work.
Wiring Diagram For A Rotary Phase Converter
A rotary phase converter is a device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). This wiring diagram for a rotary phase converter is typically complex and requires specialized skills. A qualified electrician should be able to install and wire it correctly.
Conclusion
A rotary phase converter is a device that converts AC power to a stable DC voltage. Its use in electric and motor drives. This can help you save energy and time by converting the current from AC to DC to be further utilized with engines and other devices. On the other hand, some specifications of this equipment require special attention.
For instance, while designing its circuit layout, you must keep in mind each phase’s length since they are connected end-to-end through this system. In addition, some converters come with only one control handle, allowing faster adjustments instead of relying on physical connections between phases.
Thus, if you’re looking for a more convenient solution without sacrificing reliability or performance, we recommend upgrading your old converter into a new model!
Frequently Asked Questions
[rank_math_rich_snippet id=”s-edf24a1b-b287-4c92-8933-8f7982ecb353″]

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.