Air compressors are handy in various industries, from manufacturing to construction and medical. One type of air compressor that is widely handy is the oil flooded air compressor.
They are highly efficient and provide consistent power output with minimal noise, making them ideal for industrial applications. How does an oil flooded air compressor work?? We will dive deep into the workings of an oil flooded air compressor. We will review each process step in detail, including how it utilizes oil to enhance performance.
Additionally, we will cover the benefits of using an oil flooded air compressor over other types of compressors on the market. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about these powerful machines.

What Is An Oil Flooded Air Compressor?
An oil flooded air compressor is a type of compressor that uses oil to lubricate and cool the moving parts. This type of compressor typically consists of a motor, an air tank, and a pump. The pump contains pistons or rotary screws that compress the air, while the oil acts as a lubricant to reduce friction and heat.
As the air is compressed, it passes through an oil separator to remove any oil mist before being stored in the air tank. The oil is then recirculated back to the pump for continued use. Oil-flooded air compressors are famous for their efficiency and durability, making them popular in various manufacturing, construction, and automotive industries.
Why Use An Oil Flooded Air Compressor?

An oil flooded air compressor is a popular choice for many industries and applications, and there are several reasons why it is preferred over other types of air compressors. One of the main advantages of an oil flooded air compressor is its ability to provide a continuous and reliable compressed air source.
The oil acts as a lubricant, reducing friction and wear on the internal components, which helps extend the compressor’s lifespan. The oil also helps cool down the compressed air, preventing overheating and ensuring the compressor operates efficiently.
Furthermore, an oil flooded air compressor typically produces less noise than other compressors, making it a quieter option for workplaces with minimal noise levels. Overall, using an oil flooded air compressor offers numerous performance, durability, and noise reduction benefits.
Explanation Of The Basic Components Of An Oil Flooded Air Compressor
An oil flooded air compressor consists of several key components that compress air. The first component is the inlet valve, which allows atmospheric air to enter the compressor. Once inside, the air passes through a filter to remove any impurities.
Next, the air moves into the compression chamber, which is compressed by a piston or rotor. As the air is compressed, it heats up and collects moisture. To address this, an oil separator removes excess oil and water from the compressed air.
The compressed air then moves into a storage tank or receiver, where it is stored until needed. Finally, before being released for use, the compressed air passes through a final filter to ensure it is clean and free from contaminants. Overall, an oil flooded air compressor compresses atmospheric air and removes impurities to provide clean and pressurized air for various applications.
How Does An Oil Flooded Air Compressor Work? In 6 Steps

An oil flooded air compressor uses oil to lubricate and cool the compressor’s internal components. Overall, an oil flooded air compressor relies on the lubricating properties of oil to ensure smooth operation and extend the lifespan of the compressor’s components. Here are six steps that explain how does an oil flooded air compressor work?
Compressor Operation
The air compressor draws in ambient air through the air intake, and the compressor element compresses the air, increasing its pressure. The discharge valve then releases the compressed air. During operation, the oil flood system plays a crucial role in lubricating and cooling the compressor.
Proper maintenance and monitoring ensure optimal compressor operation, enhancing energy efficiency. By understanding the compression process and the importance of the oil flood system, you can ensure the smooth functioning of your oil flooded air compressor.
Oil Reservoir
The oil reservoir of an oil flooded air compressor serves a crucial role in the system. It stores sufficient lubricating oil, providing a continuous supply to the compressor. Regular checks and refills are necessary to maintain proper oil levels, ensuring optimal performance and preventing excessive wear and tear.
Proper maintenance of the oil reservoir is essential for the longevity and efficiency of the compressor. By ensuring a steady supply of lubricant, the oil reservoir plays a vital role in the smooth operation of the compressor system.
Piston
Compressing air involves several key components in a piston oil flooded air compressor. First, the intake valve opens to allow atmospheric air into the cylinder. The piston then moves downward, creating a vacuum that draws in the air. As the piston returns upward, it compresses the air within the cylinder.
At this point, the compressor injects oil into the compressed air to lubricate and cool its internal components. The compressed air-oil mixture then flows through a separator to remove excess oil before discharge. This type of compressor is famous for its efficiency and reliability in providing high-pressure compressed air for various applications.
Air Intake And Discharge
The air intake valve in an oil flooded air compressor allows ambient air to enter the system. Once inside, the compressor element compresses the air, increasing its pressure. The discharge valve then releases the compressed air.
To ensure efficient compression and discharge, proper airflow management is crucial. Regular intake and discharge valve maintenance is also necessary for optimal compressor performance. By managing the air intake and discharge, the oil flooded air compressor can operate effectively and provide the necessary compressed air.
Air Compressor Lubrication
Lubrication is critical to the system’s operation in an oil flooded air compressor. The compressor uses oil to lubricate the moving parts, such as the piston and cylinder, to reduce friction and prevent wear and tear. The oil also helps to seal any gaps or leaks in the system, ensuring efficient operation and preventing air loss.
Additionally, the oil acts as a coolant, dissipating heat generated during compression. This helps maintain optimal operating temperatures and prolong the compressor’s lifespan. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the oil levels and quality are essential to ensure the proper functioning of an oil flooded air compressor.
Cooling
In an oil flooded air compressor, the cooling process is crucial in its operation. The compressor generates heat as it runs, and we need to dissipate it to prevent overheating. This is where the cooling system comes into play. It typically consists of a fan, a radiator, and sometimes an oil cooler.
The fan draws in ambient air and blows it across the radiator or oil cooler, which helps lower the temperature of the air and the oil. The cooled air is then directed back into the compressor, while the cooled oil is circulated back through the system to lubricate moving parts and provide additional cooling. This continuous cooling cycle ensures that the air compressor operates efficiently and prevents potential damage caused by excessive heat buildup.
Benefits Of An Oil-Flooded Air Compressor

An oil flooded air compressor is a type of compressor that uses oil to lubricate and cool its internal components. The compressor draws air through an intake valve and compresses it using a piston or rotating screw. An oil flooded air compressor offers several benefits, making it a popular choice for many applications. Here are some of the key advantages:
Enhanced lubrication: The presence of oil in the compressor helps to lubricate the moving parts, reducing friction and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Improved cooling: The oil also acts as a coolant, dissipating heat generated during compression and preventing overheating.
Increased efficiency: With proper lubrication and cooling, an oil flooded air compressor operates more efficiently, delivering higher performance and productivity.
Quieter operation: Oil helps dampen noise levels, resulting in a quieter working environment.
Better air quality: Oil-flooded compressors typically have built-in filtration systems that help remove contaminants from the compressed air, ensuring cleaner and safer air for various applications.
These benefits make oil flooded air compressors ideal for manufacturing, automotive, construction, and more industries.
Maintenance And Care Tips For Oil Flooded Air Compressors
Maintaining and caring for an oil flooded air compressor is crucial to ensure its optimal performance and longevity. By following these maintenance tips, you can prolong the lifespan of your oil flooded air compressor and ensure reliable performance for years to come. Here are some tips to help you keep your oil flooded air compressor in top condition:
- Regularly check the oil level: Oil is essential for lubricating the compressor’s moving parts. Check the oil level regularly and top it up as needed, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Change the oil and filters: Over time, the oil in the compressor can become contaminated with dirt, moisture, and other impurities. Changing the oil and filters at regular intervals is important to maintain optimal performance.
- Monitor for leaks: Look for any signs of oil leaks or excessive moisture buildup around the compressor. Leaks can lead to a loss of lubrication and affect the compressor’s efficiency.
- Clean the intake vents: Dust and debris can accumulate on the intake vents, restricting airflow and causing overheating. Regularly clean the intake vents to ensure proper ventilation.
- Inspect belts and hoses: Check the belts and hoses for any signs of wear or damage. Replace them if necessary to prevent breakdowns and ensure smooth operation.
Common Issues And Troubleshooting For Oil Flooded Air Compressors
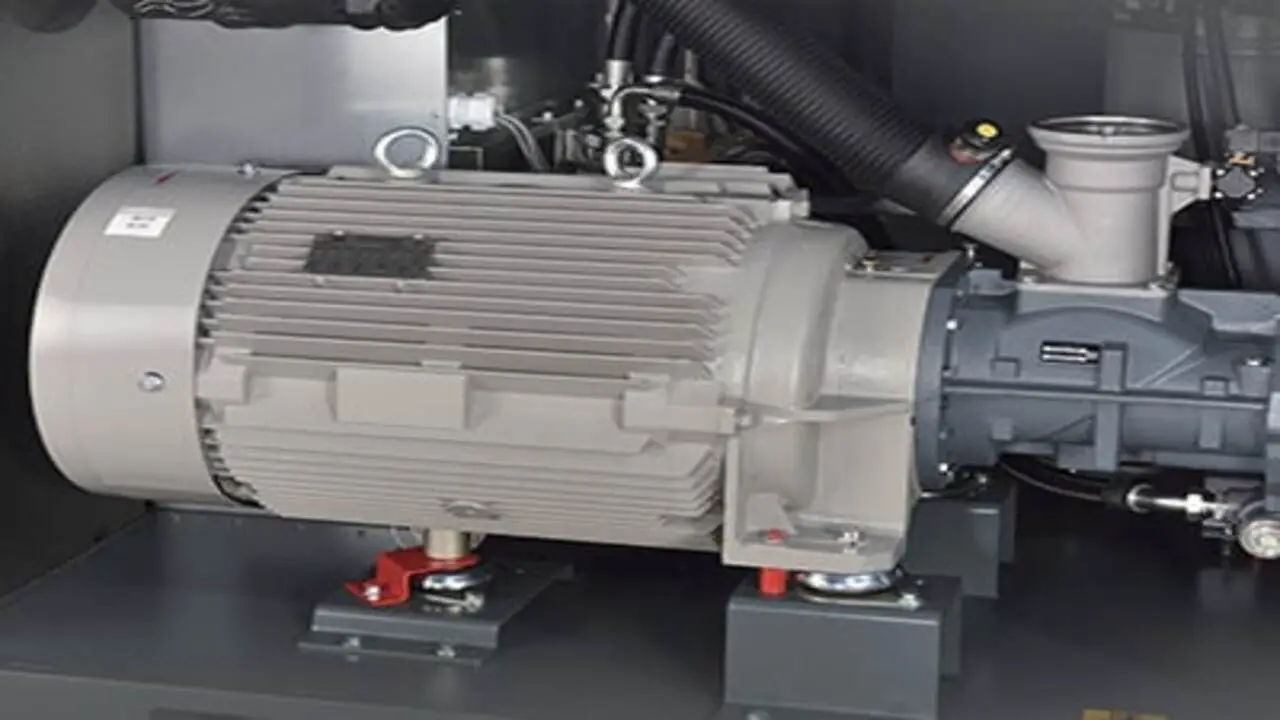

Oil-flooded air compressors are commonly handy in various industries for their efficiency and reliability. These compressors draw in air and compress it using a piston or a rotary mechanism. The key component of an oil flooded air compressor is the lubricating oil, which helps to cool and seal the compression chamber.
However, like any mechanical system, oil flooded air compressors can experience issues that may affect their performance. Here are some common problems associated with these compressors and possible troubleshooting steps:
Oil leaks: If you notice oil leaks around the compressor, it could indicate a problem with gaskets or seals. Check for loose connections or damaged components, and tighten or replace them as necessary.
Excessive oil consumption: If your compressor consumes more oil than usual, it could be due to worn piston rings or faulty valves. Inspect these components and replace them if necessary.
Overheating: Overheating can occur if the compressor’s cooling system is not functioning properly or if there is a debris buildup in the air intake. Clean the cooling system and ensure proper airflow to prevent overheating.
– Abnormal noise or vibration: Unusual noises or vibrations could indicate worn bearings, misalignment, or other mechanical issues. Inspect the compressor for any signs of damage and address the issue accordingly.
Remember to refer to the manufacturer’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps and prioritize safety when working with compressed air systems. Regular maintenance and proper care can help prevent these issues and ensure the longevity of your oil flooded air compressor.
Comparison Between Oil Flooded And Oil-Free Air Compressors
Oil-flooded air compressors use oil to lubricate and cool the compressor’s internal components. The oil is injected into the compression chamber, which helps seal the gaps between the moving parts and reduces friction. As the air is compressed, it mixes with the oil, passing through a separator to remove any oil droplets before being released into the air system.
In comparison, oil-free air compressors do not use oil for lubrication. Instead, they use other methods, such as Teflon-coated or stainless steel components, to reduce friction and prevent overheating. This makes them more suitable for applications where oil contamination is a concern, such as food processing or medical environments.
While both types of compressors have advantages and disadvantages, the choice between an oil-flooded and an oil-free compressor will depend on factors such as the specific application requirements, desired level of air purity, and maintenance considerations.
Conclusion
Understanding how does an oil flooded air compressor work? It is essential for anyone in need of compressed air. By using a combination of oil and compression, these machines can generate high-pressure air for a variety of applications. The process begins with the intake valve drawing air from the surrounding environment.
This air is then compressed by a piston or rotor, which increases the pressure and reduces the volume. At the same time, oil is injected into the compression chamber to lubricate and cool the internal components. As the compressed air exits the chamber, it passes through a separator that removes any remaining oil droplets before it can be handy. This ensures clean, dry air for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
[rank_math_rich_snippet id=”s-d433c0da-f1e2-4135-aba3-bba3de9cbb20″]

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.