Composting is the natural process of breaking down organic waste into nutrient-rich soil. It’s a sustainable way to recycle food waste and yard trimmings while reducing landfill waste.
Composting improves soil health, retains moisture, and suppresses plant diseases, promoting a healthier environment without relying on chemical fertilizers. Here we will unlock the benefits of composting and explore why is composting good for both the environment and your gardening endeavors.
Whether you’re an avid gardener looking to boost your harvest or someone passionate about sustainability, understanding the benefits of composting is key. Join us as we dive into the incredible advantages of this natural process and discover why composting is good for you and our planet.

Why Is Composting Good – Benefits Of Composting
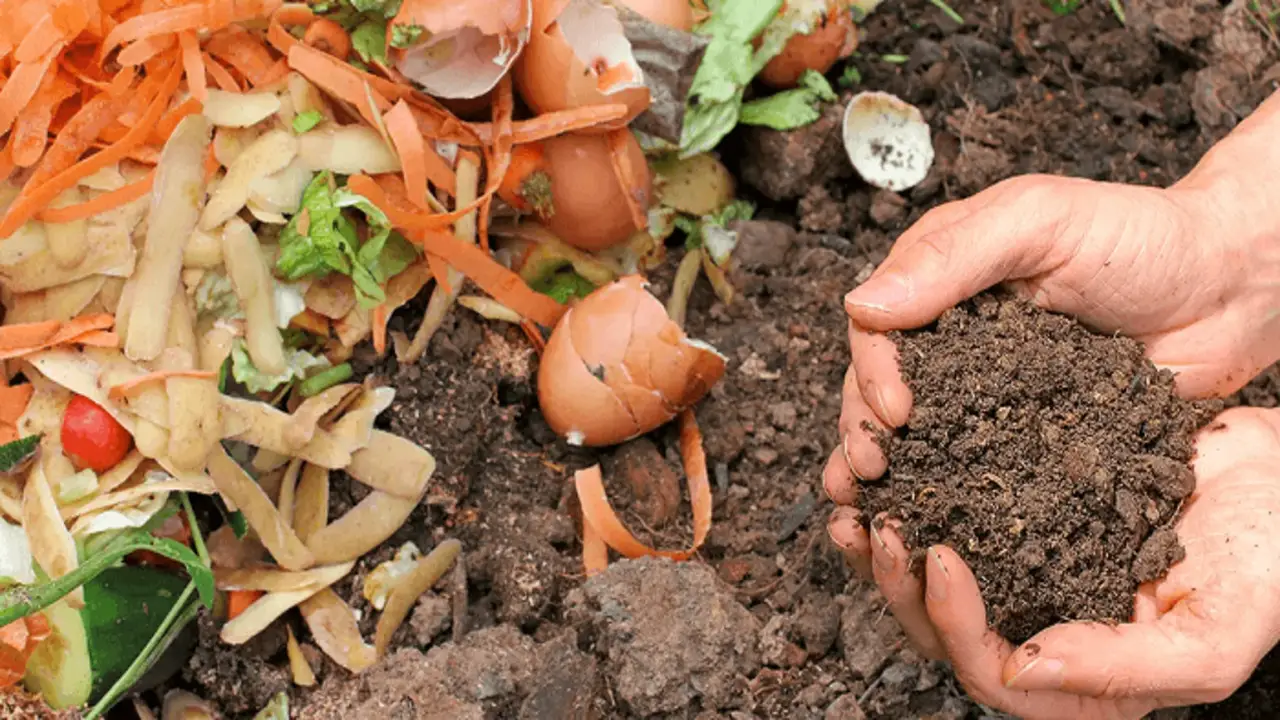

Composting offers several benefits. It reduces waste by diverting organic materials from landfills, improving recycling efforts, and reducing strain on landfill capacity. Compost enhances soil health and fertility, promoting plant growth and higher yields. It reduces the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, creating a healthier environment with lower soil and water pollution risks. Here we discuss why is composting good.
1. Promotes Carbon Sequestration
Composting is vital in promoting carbon sequestration, making it a valuable tool in the fight against climate change. By diverting organic waste from landfills, composting reduces methane gas production, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, composting enriches the soil by adding nutrients and improving its structure, ultimately leading to healthy plant growth.
This sustainable practice also helps conserve water by enhancing the soil’s moisture retention capabilities and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, promoting environmentally-friendly gardening practices. Composting truly offers an array of benefits to the environment and our gardens.
2. Increases Plant Growth And Yields
Composting enriches the soil with organic matter, providing essential nutrients for plant growth. It improves soil structure, making it easier for roots to penetrate and access water and nutrients. Compost retains moisture in the soil, reducing the need for irrigation. It helps suppress plant diseases and pests, creating a healthier growing environment.
Composting reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly gardening practices. It diverts organic waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions and contributing to waste reduction efforts.
3. Enhances Plant Nutrient Uptake
Composting enriches the soil with nutrients, making it easier for plants to absorb essential minerals. The organic matter in compost improves soil structure, allowing for better water retention and root development. Composting helps suppress plant diseases and pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
Compost acts as a natural fertilizer, promoting healthy plant growth without the use of synthetic chemicals. Recycling organic waste into compost can reduce landfill waste and contribute to a more sustainable environment.
4. Creates A Renewable Resource
Composting transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil, creating a renewable resource. This compost nourishes the soil, enhancing its health and fertility for healthier plants and higher crop yields. By diverting waste from landfills, composting reduces greenhouse gas emissions and lessens the need for chemical fertilizers.
Additionally, compost helps retain moisture in the soil, conserving water resources and reducing the need for watering. Composting also fosters beneficial microorganisms and earthworms, contributing to a healthy ecosystem and biodiversity.
5. Enhances Biodiversity

Composting promotes biodiversity by providing a habitat for microorganisms, insects, and worms that decompose organic materials. It improves soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient content, supporting plant growth and root development. Using compost as a natural and nutrient-rich alternative reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Additionally, composting reduces waste sent to landfills, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. It also saves money by reducing the need for store-bought soil amendments and promoting sustainable gardening practices.
6. Reduces Environmental Impact
Composting is crucial in reducing the environmental impact by diverting waste from landfills and minimizing methane emissions and greenhouse gases. It enriches the soil with organic matter, improving its structure, water retention, and nutrient content.
By reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides, composting promotes healthier plants and helps prevent pollution. Additionally, it aids in water conservation by enhancing the soil’s moisture-retaining capacity. Composting also mitigates the leaching of synthetic fertilizers into waterways, safeguarding aquatic ecosystems.
7. Improves Soil Quality
Composting enriches the soil by adding organic matter, improving its structure and fertility. It increases the soil’s moisture retention capacity, reducing the need for excessive watering. Compost provides essential nutrients to plants, promoting healthy growth and higher yields. Additionally, it helps suppress plant diseases and pests by encouraging a diverse microbial community in the soil. Composting contributes to a more sustainable and eco-friendly gardening practice by reducing dependence on chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
8. Increases Biodiversity

Composting promotes the growth of beneficial microorganisms, increasing the biodiversity of the soil. These microorganisms aid in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients essential for plant growth. Furthermore, composting improves soil structure, enabling roots to access water and nutrients easily.
By diverting organic waste from landfills, composting reduces methane emissions, combating climate change. Additionally, compost is a natural fertilizer, reducing the need for harmful chemical fertilizers. Through these processes, composting enhances biodiversity and contributes to a healthier environment.
9. Reduces Noise And Smell
Composting reduces waste and diverts organic materials from landfills, enriching the soil with essential nutrients for healthier gardens. It improves soil structure, making it easier for roots to access water and nutrients, promoting biodiversity with beneficial organisms like earthworms and bacteria.
Composting is an environmentally-friendly option by reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Additionally, it helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by preventing organic waste from decomposing in landfills, which produces methane gas. Composting has a positive impact on reducing noise and smell while creating nutrient-rich soil.
10. Stimulates The Growth Of Beneficial Microorganisms
Composting provides a rich source of organic matter, stimulating the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the soil. These microorganisms break down organic materials, releasing nutrients for plants to absorb. Composting also improves soil structure, making it more porous and enhancing moisture and nutrient retention.
By naturally enriching the soil, composting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. Additionally, it helps divert organic waste from landfills, preventing the production of harmful greenhouse gases. By promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms, composting plays a vital role in creating a nutrient-rich environment for plant growth.
11. Reducing Environmental Impact

Composting is essential for reducing environmental impact. It diverts organic materials from landfills, minimizing waste and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Compost improves soil health by adding nutrients and organic matter, suppressing plant diseases and pests. It also conserves water by improving moisture retention and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers. Composting promotes sustainable gardening practices.
12. Improving Soil Health
Composting enriches the soil with nutrients, making it more fertile and productive for gardening and farming. It improves soil structure, allowing for better water retention and drainage. The organic matter in compost provides food for beneficial soil organisms, such as earthworms and bacteria, which help break down organic matter and release plant nutrients.
Composting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, as nutrient-rich compost can naturally supply plants with essential nutrients. It also helps to reduce waste by diverting organic materials from landfills, which would contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills, composting also helps conserve landfill space.
13. Increasing Crop Yields
Composting enriches the soil with organic matter, improving its structure and fertility. The nutrients released from composting enhance plant growth, increasing crop yields. Composting helps protect the environment and human health by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Additionally, composting retains moisture in the soil, reducing water usage and improving drought resistance. It also diverts organic materials from landfills, reducing methane emissions and contributing to a more sustainable waste management system.
14. Preventing Water Pollution

Composting is vital in preventing water pollution by diverting organic waste from landfills. When organic waste decomposes in landfills, it releases harmful gases and leachate that can contaminate groundwater and nearby bodies of water. By composting food scraps and yard trimmings, these materials are transformed into nutrient-rich compost instead.
This compost enriches garden soil, reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, and promotes healthy plant growth. Furthermore, composting also helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and conserve landfill space. Its benefits extend beyond water pollution prevention, making it a sustainable waste management solution.
15. Producing Organic Matter
Composting is a natural process that transforms organic waste into nutrient-rich soil known as compost. This valuable resource improves soil health and fertility, making it ideal for gardening and farming. Composting can reduce landfill waste, contributing to a more sustainable waste management system and reducing methane emissions contributing to climate change.
Composting also enhances water retention in the soil, conserving water and improving drought resistance. Using compost in your garden promotes healthy plant growth, increases crop yields, and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
16. Improving Soil Fertility
Composting offers numerous benefits for improving soil fertility. Adding organic matter through composting enhances the soil’s structure, allowing it to retain water and nutrients more effectively. This reduces the dependency on synthetic fertilizers as compost naturally provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
Additionally, composting diverts organic materials from landfills, where they would produce methane gas, a potent greenhouse gas. It also promotes biodiversity by creating a favorable environment for beneficial microorganisms, worms, and insects that support plant growth. Compost can even help suppress plant diseases and pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Furthermore, compost improves moisture retention, conserving water and reducing irrigation frequency.
Conclusion
Composting is a sustainable practice and an essential step in creating a healthier planet. The benefits of composting are vast and have far-reaching effects. Composting helps reduce environmental impact by diverting organic waste from landfills, where it would otherwise produce harmful greenhouse gases. Additionally, compost improves soil quality by increasing its nutrient content and enhancing its ability to retain moisture.
This, in turn, promotes plant growth and increases biodiversity. By participating in composting, individuals can actively contribute to carbon sequestration, create a renewable resource, and play a crucial role in building a greener future for future generations. It’s time to unlock the numerous benefits of composting and start positively impacting our environment. Hope the above outline on why is composting good will help you to enhance your composting knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
[rank_math_rich_snippet id=”s-f0690f57-21de-498a-bbbd-e8573beacc7c”]

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.








