Raised beds are a popular gardening technique involving growing plants in soil elevated above ground level. This method has many benefits, including improved drainage, reduced soil compaction, and better access for gardeners with limited mobility.
There are many benefits to using raised beds in your garden, including improved drainage, better soil quality, and easier access to planting and maintenance. Are you looking for a sustainable way to fertilize your raised beds? Not only does it nourish plants, but it also reduces waste and helps the environment. We will explain the science behind composting, how to start composting in raised beds, and what tools you need.
However, we will also cover planting in Composting in Raised Beds and the benefits of composted soil. We will also discuss common mistakes to avoid when composting and how long it takes to break down and fully become usable. So grab your gardening gloves, and let’s get started on creating nutrient-rich soil for your plants.

Understanding The Composting Process
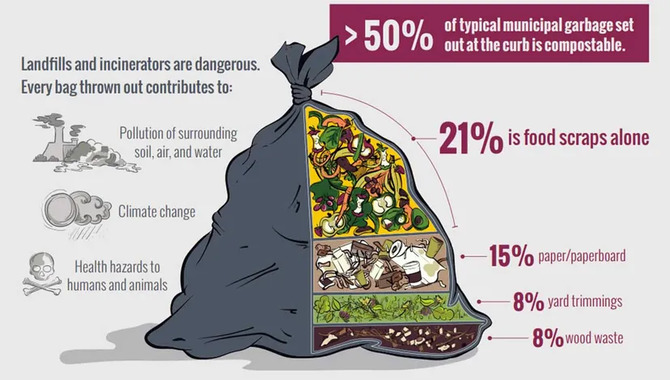
Composting is a natural process that involves the breakdown of organic material, such as food scraps and yard waste, into nutrient-rich soil. The process begins when microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and worms, break the organic matter into smaller pieces.
As these microorganisms consume the organic matter, they release carbon dioxide and heat, which helps to break down the material further. Over time, the organic matter transforms into a dark, crumbly substance called compost.
The key to successful composting is creating the right organic material, moisture, oxygen, and temperature balance. A good rule of thumb is to aim for a ratio of about 3 parts of “brown” materials (such as leaves or straw) to 1 part of “green” materials (such as food scraps or grass clippings).
It’s also important to keep the compost pile moist but not too wet and to turn it regularly to aerate it and maintain a consistent temperature. By understanding the composting process and following a few basic guidelines, anyone can create nutrient-rich soil for their garden. Or lawn while reducing their environmental footprint by diverting organic waste from landfills.
Explanation Of The Dirt On Composting In Raised Beds

The Dirt on Composting in Raised Beds is an informative guide that explains the benefits of composting and how to do it effectively in raised beds. Composting is a natural process where organic materials such as food scraps, leaves. And grass clippings break down over time to create a nutrient-rich soil amendment. By adding compost to raised beds, gardeners can improve soil health, increase plant growth and yield, and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers.
The guide provides step-by-step instructions on creating a compost pile. What materials are suitable for composting, and how to maintain the right balance of nitrogen and carbon? It also discusses the importance of turning the compost pile regularly to ensure proper decomposition.
One of the key advantages of using raised beds for composting is that it allows gardeners to control the quality and quantity of compost produced. This means that they can tailor their compost mix to suit the specific needs of their plants. Overall, The Dirt on Composting in Raised Beds is an essential resource for any gardener looking to improve soil health and grow healthy, vibrant plants.
What Tools Do I Need To Start Composting In Raised Beds?

Starting a compost in your raised beds is a great way to improve soil health and reduce waste. To get started, you will need a few essential tools. First, you will need a compost bin or container to hold the organic materials. You can purchase one or make your own using wire mesh or wooden pallets. Second, you will need a pitchfork or shovel to turn and mix the compost regularly. This helps to aerate the pile and speed up the decomposition process.
Third, you may want to invest in a compost thermometer to monitor the temperature of the pile and ensure that it stays within the ideal range for decomposition. Finally, gloves and a mask are recommended for handling the organic materials and avoiding potential allergens or harmful bacteria. With these tools, you can start your own compost in raised beds and reap the benefits of healthier soil for your garden.
How To Start Composting In Raised Beds

Composting in raised beds is an easy and effective way to improve soil quality and reduce waste. The first step is to choose a location for your compost bin or pile. It should be in a well-draining area with easy access. Next, you’ll need to gather materials such as food scraps, yard waste, and dry leaves or straws.
Layer these materials in the bin or pile, making sure to include both nitrogen-rich “greens” and carbon-rich “browns.” Turn the compost regularly to ensure proper aeration and moisture levels. As the compost breaks down, it will provide nutrients to your raised bed plants and improve the overall health of your garden. With a little effort and patience, starting composting in raised beds can be a rewarding and sustainable practice for any gardener.
Choosing The Right Composting Container

Successful composting in raised beds depends on selecting the right container for efficient decomposition. Size, material quality and ventilation are crucial factors you should consider. If you’re looking for an effortless method with fast results, consider using a worm composter or a compost tumbler.
But make sure to pay attention to your specific gardening needs before settling on one! With the appropriate composting container, you can ensure proper drainage, aeration and nutrition for your plants.
Adding Scraps And Topsoil To The Bin
Creating nutrient-rich soil for your raised bed by adding scraps and topsoil to the bin is an excellent idea. This process is critical to balancing the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio by layering kitchen scraps and yard waste with topsoil.
While you add garden clippings or grass clippings to your compost pile throughout the growing season, ensure a good amount of moisture is present. However, avoid adding meat, dairy, or oily foods as they can attract pests and slow composting. Regular turning and aerating of your compost can also help speed up decomposition.
Using Worms To Aid Composting
Adding earthworms to your compost pile is an excellent technique for promoting decomposition and enhancing soil quality in raised garden beds. Red wigglers are the most commonly used type of worm in composting because they break down organic matter quickly. To ensure that your worms thrive, make sure that their environment has plenty of moisture and ventilation.
Remember to exclude dairy, meat, or oily foods from your compost, which will attract pests or slow down the process. Incorporating earthworms into your composting routine is an easy way to create rich soil with plenty of nutrients for growing healthy plants next season.
Planting In Composted Raised Beds

Mixing nutrient-rich compost evenly throughout the garden soil of your raised beds can provide the best conditions for growing plants. Choosing plants that suit your sunlight and water requirements is crucial when planting in raised garden beds with compost.
Maintaining soil fertility by regularly adding new compost will ensure you have healthy, thriving plants all year round. Remember not to add dairy or oily foods to your bin as they attract pests and slow decomposition. Incorporating organic matter such as grass clippings, leaves, eggshells, and coffee grounds can help maintain a balanced nitrogen-to-carbon ratio, speeding up the decomposition process.
Trenching Vs. Layering
Regarding Composting in Raised Beds, two methods stand out- Trenching and Layering. The former involves digging a trench in your garden bed and filling it with organic matter before planting. The latter refers to spreading the compost over the topsoil and planting your seeds.
While Trenching improves soil structure by providing essential nutrients to plant roots, Layering saves time but may require more frequent applications of mulch or compost throughout the growing season. So whether you choose Trench Composting or Sheet Composting, make sure. It works well for your raised bed by considering factors such as Soil Structure and Nutrient requirements.
Using Compost As A Top Dressing
Maximize nutrition while improving drainage and aeration in your garden bed without disturbing your plants’ roots or exposing seeds to pests and weeds. Using compost as a top dressing is an excellent solution!
Apply about an inch of high-quality compost- rich in nitrogen- all over your garden bed from the base of each plant to cover the entire bed uniformly. The added layer of compost acts like a protective shield that moistens the soil while enriching it with vital nutrients for healthy plant growth.
Shrubs That Benefit From Composted Soil

Adding composted soil to a raised garden bed can do wonders for shrubs like blueberries, roses, and hydrangeas. It increases nutrition and drainage while releasing heat that lengthens the growing season. Mix thoroughly before planting and avoid nitrogen overload.
Regular top-dressing of high-quality compost with plenty of organic materials leads to healthy. Productive plants thrive even in new beds or during next spring’s perennials’ bloom. Don’t forget to layer carefully to prevent root stress from too much mulch or moisture.
The Benefits Of Composting In Raised Beds

Gardeners can benefit from composting in raised beds as it improves soil fertility and structure, resulting in better plant growth and higher yields. This method is an environmentally friendly alternative to sending waste to landfills. Composting in raised beds reduces water usage by retaining moisture in the soil, ultimately supporting plant life. The use of compost instead of chemical fertilizers leads to a more natural approach to gardening.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Composting In Raised Beds
When it comes to composting in raised beds, there are a few common mistakes that gardeners should avoid. One of the biggest mistakes is adding too much carbon-rich material, such as leaves and straw, without enough nitrogen-rich material, such as kitchen scraps or manure.
This can result in a slow decomposition process and an imbalance in the compost’s nutrient content. Another mistake is not turning the compost frequently enough, which can lead to anaerobic conditions and unpleasant odors.
It’s also important to avoid adding meat, dairy, or oily foods to the compost as they can attract pests and slow decomposition. Lastly, it’s essential to ensure that the temperature of the compost remains between 120-150°F for optimal decomposition. By avoiding these common mistakes and following best practices for composting in raised beds, gardeners can create nutrient-rich soil for their plants while reducing waste.
How Long Does It Take For Compost To Fully Break Down And Become Usable?
Composting is a great way to reduce waste and create nutrient-rich soil for your garden. The process of composting involves breaking down organic matter, such as food scraps, leaves, and grass clippings, into a dark, crumbly substance called humus. The length of time it takes for compost to fully break down and become usable.
Depends on various factors, such as temperature, moisture levels, and the type of materials being composted. In general, compost can take anywhere from several weeks to several months to fully decompose. However, with proper care and attention, you can speed up the process and produce high-quality compost in as little as three to four weeks.
The key is maintaining the right balance of carbon-rich “brown” materials, such. as dried leaves or straw and nitrogen-rich “green” materials, such as food scraps or grass clippings. While keeping the pile moist but not too wet. With a little patience and effort, you can turn your kitchen scraps and yard waste into a valuable resource for your garden.
Conclusion
Composting in raised beds is one of the best ways to create nutrient-rich soil for your plants. It’s a simple and effective way to recycle organic waste while improving the environment and reducing landfill waste. With the right tools and techniques, you can easily start composting in your raised beds today.
But avoiding common mistakes like adding meat or dairy products is important, which can attract pests and slow composting. Adding organic matter to your raised beds can create a nutrient-rich environment that supports healthy plant growth and maximizes yields.
Additionally, composting in raised beds helps to reduce waste and promote sustainability by recycling organic materials. Composting takes time, so be patient as you wait for your organic waste to break into usable soil. Start composting today and reap the benefits of healthy soil and bountiful harvests.
Frequently Asked Questions
[rank_math_rich_snippet id=”s-582839f2-8d56-4fc2-8fcb-36353f091ad5″]

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.
