If you’ve ever wanted to grow a bonsai tree but weren’t sure how to go about it, this blog is for you. In this article, we’ll be discussing the basics of grafting – what it is, how it works, and some of the purposes it can serve. By the end of this post, you should be well-equipped to attempt grafting yourself!

What Is Grafting?
Grafting is the process of transferring a root or branch from one tree to another so the two can share resources and grow together. There are many types of grafting materials you can use depending on the type of plant you are grafting onto.
For bonsai trees, grafting is an effective way to move them from one location to another and to grow larger trees. If you’re unsure about how to do grafting, consult with a professional before starting. G
rafting is an easy way to move a bonsai tree from one location to another, and it’s also effective for growing larger trees. So, whether you’re looking to move a bonsai tree to a new spot or to help it grow bigger, grafting is the perfect solution!
How Does Grafting Work?

If you’re looking to take your bonsai tree skills up a notch, grafting might be the perfect option for you. Grafting can result in more robust plants with better foliage than traditional plant breeding techniques.
It is a process of transferring a branch or root of a tree to another tree. Which can help growing plants that aren’t genetically compatible to grow together. Can share resources like water and sunlight.
If you are interested in grafting your own bonsai tree, be sure to have the right tools and knowledge first! Grafting is a complex process, so it’s important to have someone who can guide you through the process and make sure you get the results you’re looking for.
Types Of Grafting
Grafting is a process that allows two different trees to be connected using a union. There are two types of grafting – piece and whip. Piece grafting is the most common, as it’s less invasive. To graft a bonsai tree, you’ll need a few supplies – a knife, a scion (the donor tree), water, and rooting hormone/sealant.
Follow these simple steps to start: cut off a small section from the desired tree; clean the wound; insert the scion into the wound so that its root is above water level; wait 24 hours while roots grow down into the soil; apply to root hormone/sealant to both sides of plant junction (just below stem); attach new branch or twig using the needle-and-thread method.
Piece grafting is the process of attaching a new branch or twig to a bonsai tree using a union. Whipping grafting is the process of attaching a new branch or twig to a bonsai tree by pulling it through the bark of the donor tree. It’s more invasive, but results in stronger plants with better foliage development.
1. Rooting Methods

There are three types of grafting – stem, twig, and leaf. The most common rooting method used is ‘knot planting’, which involves tying a knot in the root ball and burying it below ground level. This process makes use of the tree’s new growth to help anchor the plant in place.
They work by taking a piece from a tree and attaching it to another tree to change its shape or appearance. Simply put, this is how grafting helps plants grow together. So that they can withstand harsh weather conditions or any other challenges that life throws their way!
2. Overview
Grafting is the process of transferring plants from one tree to another. The graft union, or semi-union graft, is the most common type of graft used in landscape and horticulture. This involves inserting an incision into the bark. And then cut a portion of the rootstock that will meet the cambium (woody layer) of the grafted branch/plant.
This method has several advantages over other types of grafts. It’s quick and easy to do, doesn’t damage the plant too much, and minimizes transplant shock. Meristem grafting is less commonly used but offers some significant advantages. It is a more difficult incision to make, so there is less chance of error during surgery.
This allows for more control over how the two plants are joined together. And this results in stronger plants because further growth can occur at multiple points along the meristem rather than just at the graft union.
3. Application Of Grafting

Grafting is the process of connecting two different pieces of wood together. You can do it in different ways. However, veneer and stem grafting are the most common. Veneer grafting is used to join two pieces of wood together, while stem grafting is used to join different parts of the same tree. Both methods require a fair amount of skill and practice.
It’s best to seek out help from a professional if you’re unsure about how to do it yourself. Both types are successful in increasing plant strength and stability. As well as adding new dimensions or shapes to an existing tree. There’s no wrong choice when deciding which type will work better for your project!
Preparation For Grafting
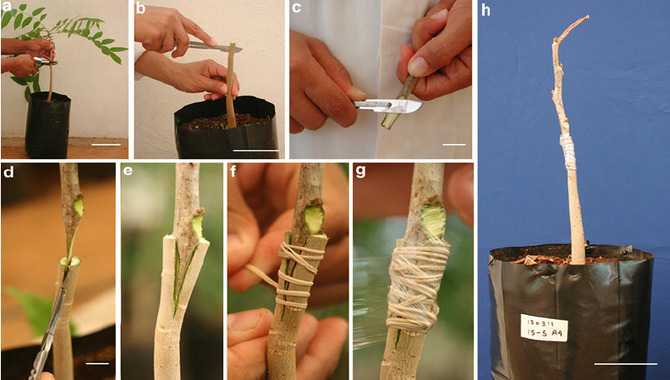
Grafting a bonsai tree is a delicate process that requires a lot of preparation. Before you even start, be sure to remove any dead or diseased branches. Then, plant each plant in its new location. And trim any excess leaves around the base of the trunk. So that only 1/2-1 inch grows from the soil level from both plants.
Make cuts on both plants where you will make incisions to insert the branches and close the wounds with twine or thread bandage material.. Be careful not to nick the bark, and make sure to read the plant’s care instructions carefully before starting grafting. When grafting is complete, be sure to water the trees well and keep them in a well-lit area.
How To Do The Actual Grafting
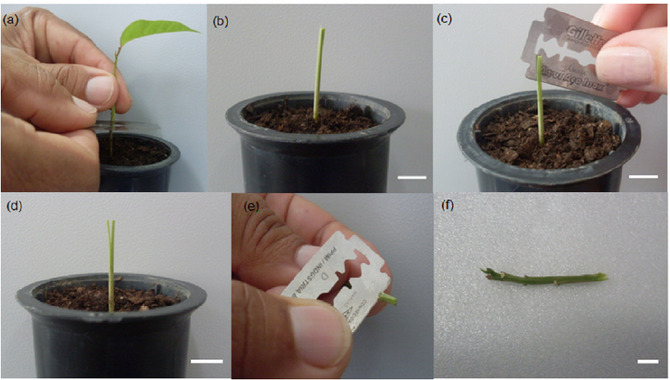
Grafting is the process of transferring a cutting from one plant to another. Usually with the aim of increasing the structural stability or strength of the recipient plant. It is important to make sure that the tree you want to graft is strong and healthy and has healthy branches for grafting.
Once you have selected your tree, remove any dead or diseased branches before starting the grafting process. Next, cut a small branch from your desired tree and place it into a pot of water so that it can start rooting. Make sure both ends of the branch are thoroughly wet.
This will help ensure good contact between them while grafting to each other. Finally, using a sharp knife carefully graft both surfaces of the branch together making sure not to damage either part too much while doing so!
Techniques For Grafting

Grafting is the process of attaching two trees together so that they share resources and grow together harmoniously. It can be a bit daunting at first, but with the right techniques and preparation, grafting can be a success. To maximize the chances of a successful graft.
Make sure to wait until after the new growth has stopped on both trees before doing anything. Additionally, choose a tree that has a good root system for the plant you’re grafting onto. This will affect success rates significantly. There are several techniques you can use to graft, such as whip-cutting or cedar wax treatment. Once you have a good understanding of grafting, get grafting!
Conclusion
Grafting is the process of transferring a scion (the cutting bud of a tree or other plant) to the rootstock (a tree or other plant to which you want to graft). The scion will take root in the rootstock and the two plants will be connected by a layer of cambium (a layer of living cells).
which helps in the transfer of water and nutrients between plants. Grafting is an effective way to transfer trees, shrubs, and other plants from one place to another. And also used to create new bonsai trees. Please keep reading to learn more about grafting and how it works!
Frequently Asked Questions
[rank_math_rich_snippet id=”s-74ff2dc8-de4e-4f91-9bad-41e573188c86″]

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.








