Composting for vegetable gardens is the key to achieving healthy, nutrient-rich soil that will result in bountiful harvests.
However, composting gardens is a method of decomposing organic materials to produce nutrient-rich soil. Composting enhances soil structure and fertility by combining kitchen scraps, leaves, and grass clippings, creating an ideal environment for plant growth. Adding compost to vegetable gardens enriches the soil and supplies vital nutrients for plants.
Here we will cover everything you need to know about composting for gardens. Step-by-step instructions on how to start your own compost pile or bin. We will provide tips on choosing the right composter and using compost in your vegetable garden effectively. Get ready to transform your gardening game with the power of composting.

How To Composting For Vegetable Gardens – 8 Easy Steps

Composting for vegetable gardens is essential to maintain the health and productivity of plants. Composting provides a natural and sustainable approach to support optimal plant growth by enriching the soil with vital nutrients.
It aids in moisture retention, reducing the reliance on frequent watering. Moreover, composting enhances soil structure, facilitating easy root penetration for plants. Here are the full process of composting gardens.
1. Select A Suitable Location
Choosing the right location is crucial for composting in vegetable gardens. Consider convenience, but avoid placing it too close to the garden to prevent pests. Partial sun exposure is beneficial, so find an area with sunlight. Good drainage is important to ensure ideal composting conditions. For a more organized setup, use a compost bin or container.
2. Gather Materials
To begin composting for gardens, gather various organic materials comprising nitrogen-rich greens and carbon-rich browns. Greens include common kitchen scraps, grass clippings, and fresh plant trimmings, while browns consist of dried leaves, straws, and cardboard.
Consider complementing your mix with coffee grounds, eggshells, or shredded newspaper. Layer these materials in a compost bin or pile, maintaining a balance between greens and browns for successful decomposition.
3. Prepare The Compost Bin Or Pile

To prepare your vegetable garden’s compost bin or pile, choose a suitable location that’s easily accessible. Opt for an area that receives partial sun to aid decomposition. Avoid placing it too close to your vegetable garden to prevent attracting pests. Good drainage is essential to avoid waterlogging. Consider using a compost bin or container for a tidy setup.
Gather the necessary materials for your compost, including a mix of green and brown organic matter. Green materials, like kitchen scraps and grass clippings, are nitrogen-rich. Whereas brown materials, like dried leaves and cardboard, contain carbon. Layer these materials in your compost bin or pile.
4. Turn The Compost
To successfully compost for vegetable gardens, regularly turn the compost pile to aerate it and speed up decomposition. This creates nutrient-rich humus for your plants. Use a garden fork or shovel to gently mix the outer and inner layers, distributing moisture evenly and promoting decomposition.
Turn the compost every 2-3 weeks, ensuring proper mixing and aeration. Wear gloves for protection from sharp objects. Regular turning will provide abundant organic matter to enrich your vegetable garden.
5. Monitor Moisture Levels
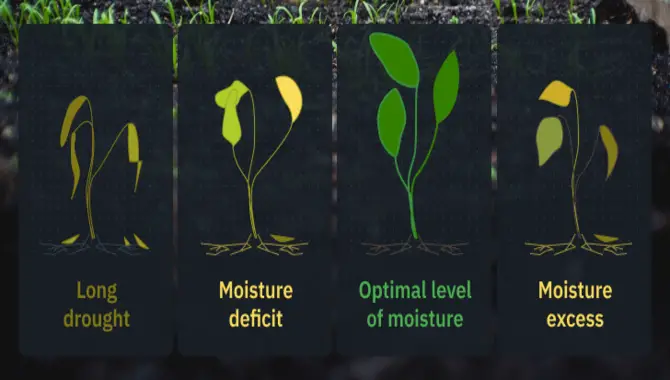
To ensure successful composting in vegetable gardens, monitoring the moisture levels in your compost pile or bin is crucial. Maintaining proper moisture is essential for the breakdown of organic matter and the promotion of decomposition. Optimal moisture levels are similar to a squeezed sponge – damp but not soggy.
If the compost becomes too dry, it may impede proper breakdown, making adding water for adequate moisture necessary. Conversely, it may emit odours and attract pests if it becomes too wet. In such cases, incorporating dry materials like leaves or shredded newspaper will help absorb excess moisture, ensuring a balanced environment for composting. Regularly checking and adjusting moisture levels can create the perfect conditions for composting in your vegetable garden.
6. Maintain The Pile
Properly maintaining your compost pile is crucial for successful decomposition in your vegetable garden. Regularly mix the materials to provide oxygen and ensure they are well-aerated. Keep the compost moist, like a damp sponge, but be cautious not to make it too wet. If it becomes too dry, add water to maintain moisture levels.
If it becomes too wet, add dry materials like leaves or straw to absorb excess moisture and prevent odors. The ideal temperature for the compost pile should range between 135-160 degrees Fahrenheit to kill off weed seeds and harmful pathogens. Introduce new organic materials such as kitchen scraps, yard waste, and shredded paper to keep the compost active and balanced. Avoid including meat, dairy products, or oily foods to maintain a healthy and odour-free process.
7. Compost Maturity

Compost maturity is when compost is fully decomposed and ready for use in the vegetable garden. This stage typically takes months, depending on temperature, moisture, and materials. Signs of maturity include the absence of recognizable organic materials, an earthy smell, and a temperature similar to the surroundings.
Using mature compost is crucial for healthy plant growth and preventing weed seeds or pathogens. If your compost isn’t yet mature, continue to aerate and turn it regularly to speed up decomposition.
8. Harvest The Compost

Composting is an important way to dispose of organic waste and improve soil in vegetable gardens. Harvest the compost once it has decomposed into a dark, crumbly material. Use gloves and protective clothing when handling the compost. Spread it over your garden beds as a nutrient-rich soil amendment or store it for future use. Compost successfully for your vegetable garden with these tips!
Composting Benefits
Composting offers a range of benefits for vegetable gardens. composting provides a favourable environment for vegetable plants to flourish by enriching the soil with nutrients. It also aids in retaining soil moisture, reducing the need for excessive watering. Compost enhances soil structure, facilitating strong root establishment and promoting optimal plant growth.
Moreover, composting helps mitigate the negative environmental impact of organic waste in landfills, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Using compost as a natural fertilizer results in healthier plant growth and increased yields in vegetable gardens.
Soil Conditioner

Composting is crucial for improving soil structure and fertility in vegetable gardening. It enriches the soil with nutrients and promotes a healthy environment for plant growth. Composting reduces waste, retains moisture, and provides slow-release nutrients for healthier plants and higher yields in your vegetable garden. Improve soil structure, moisture retention, and overall plant health by incorporating compost into your garden.
Recycles Kitchen And Yard Waste
Composting kitchen and yard waste reduces landfill waste and enriches your vegetable garden. Instead of throwing away food scraps, grass clippings, and garden waste, compost them to create nutrient-rich soil. Composting improves soil quality, moisture retention, and nutrient availability.
It also reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers and promotes sustainable gardening. Composting reduces waste and greenhouse gas emissions and promotes healthy plant growth in your vegetable garden.
Introduces Beneficial Organisms To The Soil
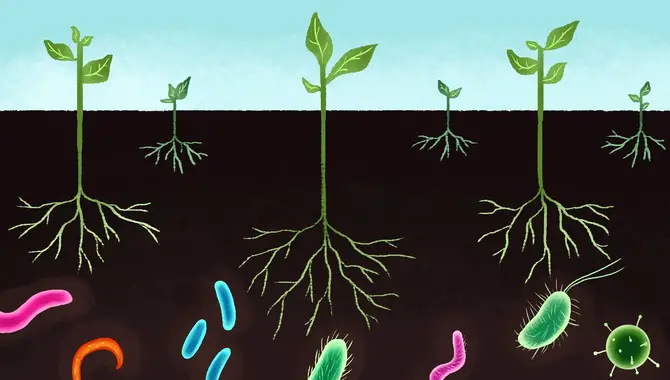
To compost effectively for vegetable gardens, it is important to introduce beneficial organisms to the soil. These microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and earthworms, break down organic matter and create nutrient-rich compost.
They improve soil structure and fertility, creating an ideal environment for plant growth. Using compost in your vegetable garden enhances plant health without relying on synthetic fertilizers. This natural approach enriches the soil, suppresses harmful pathogens and pests, and promotes sustainable gardening. Introducing beneficial organisms is crucial for a thriving garden ecosystem.
Good For The Environment
Composting offers many environmental benefits, making it a sustainable choice for vegetable gardens. Not only does it reduce landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions, but it also improves soil structure, aeration, and water retention.
Composting introduces beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria and worms, to the soil, aiding the decomposition process and promoting healthy plant growth. Using compost in your garden can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, further minimizing the environmental impact. Composting is a simple yet effective way to create nutrient-rich soil for your vegetable garden while minimizing waste.
Reduces Landfill Waste

Composting reduces landfill waste and its impact on the environment. It decreases methane gas production by diverting organic waste from landfills. Gardeners can transform kitchen scraps, garden waste, and yard clippings into nutrient-rich compost for vegetable gardens. This sustainable practice improves soil health, promotes plant growth, retains moisture, and enhances soil fertility.
How To Choose A Composter
Choosing the best composter is an essential step in successful composting gardens. Ensuring the right tool to handle your organic waste is vital for optimal results. Consider size, capacity, and construction materials when selecting a composter. Look for durable options that can withstand the composting process.
Aeration features, such as ventilation or rotating mechanisms, promote decomposition. Easy maintenance and usability are important for hassle-free composting. Take the time to research customer reviews and ratings to make an informed decision. Following these guidelines, you’ll find the ideal composter to create nutrient-rich compost for your vegetable garden.
How To Use Composting In Vegetable Gardens

Composting in vegetable gardens enhances soil fertility and promotes sustainable gardening. You can create nutrient-rich compost by decomposing organic materials like kitchen scraps and yard waste. Layering the pile with green and brown materials is important.
Regularly turning and watering the pile facilitates decomposition, resulting in fine compost. Adding this compost to your vegetable garden improves soil structure, drainage, and moisture retention for healthier plants and higher yields. Embrace composting as a gardener for remarkable benefits in your vegetable garden.
Conclusion
Composting for vegetable gardens is crucial to ensure healthy and abundant yields. Creating a compost pile or bin can recycle kitchen and yard waste, turning it into a nutrient-rich soil conditioner. To start composting, select a suitable location, gather materials like food scraps and yard waste, and prepare the compost bin or pile. Turn the compost regularly, monitor moisture levels, and maintain the pile. Once the compost reaches maturity, you can harvest it and use it in your vegetable garden.
The benefits of composting are numerous. It improves soil condition by adding essential nutrients, introduces beneficial organisms that enhance plant growth, and reduces the need for chemical fertilizers. Composting also helps recycle waste and reduce landfill waste, making it an environmentally friendly practice.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.What Is The Best Way To Compost For A Vegetable Garden?
Ans: For a successful vegetable garden compost, begin with a balanced mix of green (vegetable scraps, grass clippings, coffee grounds) and brown materials (dry leaves, straw, shredded newspaper). Regularly turn the pile to promote decomposition and prevent unpleasant odors.
2.What Vegetable Should Not Be Composted?
Ans: Avoid composting meat, dairy, and oily foods that attract pests for a healthy compost pile. Onions, garlic, and citrus peels can disrupt the compost balance. Also, avoid composting diseased or pest-infested vegetables, invasive weeds, or plants with seeds that could spread in your garden.
3.Can I Grow Vegetables In Straight Compost?
Ans: Growing vegetables in straight compost is not advisable as it lacks the essential balance of nutrients for healthy plant growth. It’s recommended to mix compost with soil in a ratio of 1 part compost to 2 parts soil to create a nutrient-rich growing medium suitable for vegetable gardening.
4.Should I Add Compost To My Vegetable Garden?
Ans: Absolutely! Adding compost to your vegetable garden is a fantastic idea. It enriches the soil by improving its fertility, structure, and nutrient content. Additionally, compost helps retain moisture and supports healthy root growth. It even introduces beneficial microorganisms that boost plant growth and disease resistance.
5.Why Is Organic Compost Best For Vegetable Gardening?
Ans: Organic compost is the ideal choice for vegetable gardening because it enhances soil structure and fertility. It releases essential nutrients slowly and retains moisture in the soil, reducing watering needs. Additionally, organic compost promotes beneficial microbial activity, improving plant health and disease resistance.

I am passionate about home engineering. I specialize in designing, installing, and maintaining heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. My goal is to help people stay comfortable in their homes all year long.
